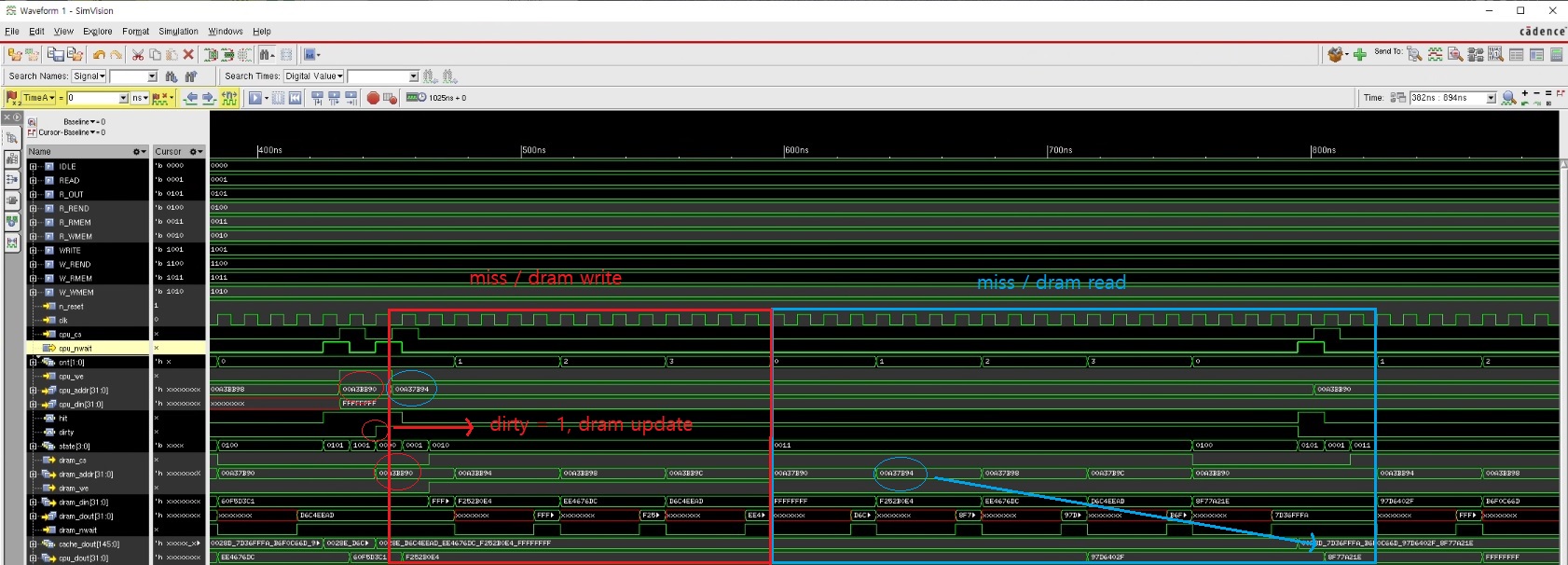
진행년월: 24.08
목차
1. 배경
2. 과제 정의 및 개요
3. 소스코드
4. 결과
1. 배경
Convolution 연산은 신호 처리 부분에서 많이 사용합니다.
특히, Filtering이 주된 용도이고, HPF, LPF가 있겠죠.
저는 이번에 2차원 Filter를 이해하고 설계해본 뒤에
그것을 확장하여 이미지 처리 모델인 CNN을 구현해보려고 합니다.
2. 과제 정의 및 개요
제가 사용할 필터는 아래와 같으며, LPF(Low Pass Filter) 입니다.

위 필터는 중심을 기준으로 평균화해줍니다.
원본 이미지와 필터링된 이미지를 먼저 보면,

좌측(원본)이 조금 뚜렷하고, 우측(필터링)은 일종의 블러효과를 넣은 것처럼 흐릿해졌습니다.
A = imread('lena_gray.png');
B = imresize(A, 0.5);
dlmwrite('img_in.txt',B);
MATLAB을 통해 512 X 512 size 원본 이미지를 256 X 256 size로 조절한 뒤 저장하였습니다.
이제 이것이 input image가 될 것입니다.
전체 Process
1. C코드로 먼저 Fixed Point로 변환 및 구현하며, 입력, 출력 예시를 준비
2. Verilog 구현
3. Double Buffering으로 데이터 충돌 방지
4. Line Buffering으로 입력과 동시에 처리해 Cycle
5. Parameterizing, Testbench에서 DPI를 통한 C코드 활용
3. 소스코드
- 3.1 C코드 구현
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
void filter2d(unsigned char in_img[], unsigned char out_img[],
int height, int width) {
int h[3][3] = {0x08, 0x10, 0x08, 0x10, 0x20, 0x10, 0x08, 0x10, 0x08};
for(int i=0;i<height;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<width;j++) {
int sum = 0;
if(i>0 && j>0) sum += in_img[(i-1)*width+j-1]*h[0][0];
if(i>0) sum += in_img[(i-1)*width+j ]*h[0][1];
if(i>0 && j<width-1) sum += in_img[(i-1)*width+j+1]*h[0][2];
if(j>0) sum += in_img[(i )*width+j-1]*h[1][0];
sum += in_img[(i )*width+j ]*h[1][1];
if(j<width-1) sum += in_img[(i )*width+j+1]*h[1][2];
if(i<height-1 && j>0) sum += in_img[(i+1)*width+j-1]*h[2][0];
if(i<height-1) sum += in_img[(i+1)*width+j ]*h[2][1];
if(i<height-1 && j<width-1) sum += in_img[(i+1)*width+j+1]*h[2][2];
sum = (sum + (1<<6)) >> 7;
if(sum < 0) out_img[i*width+j] = 0;
else if(sum > 255) out_img[i*width+j] = 255;
else out_img[i*width+j] = sum;
}
}
}
int main(void) {
int i, a;
FILE *inf, *outf, *memf;
unsigned char in_img[256*256];
unsigned char out_img[256*256];
inf = fopen("img_in.txt", "r");
outf = fopen("img_out.txt", "w");
memf = fopen("img_in.dat", "w");
for(i=0;i<256*256;i++) {
fscanf(inf, "%d,", &a);
in_img[i] = a;
fprintf(memf, "%02X\n", in_img[i]);
}
filter2d(in_img, out_img, 256, 256);
for(i=0;i<256*256;i++) {
fprintf(outf, "%3d ", out_img[i]);
if(i%256 == 255) fprintf(outf, "\n");
}
fclose(inf);
fclose(outf);
fclose(memf);
}
- 3.2 Verilog 구현

module filter2d (
input clk,
input n_reset,
input start,
output reg finish,
output cs,
output we,
output [16:0] addr,
output [7:0] din,
input [7:0] dout,
input h_write,
input [3:0] h_idx,
input [7:0] h_data
);
reg on_proc;
reg [3:0] cnt;
reg [7:0] cnt_x;
reg [7:0] cnt_y;
always@(posedge clk or negedge n_reset) begin
if(n_reset == 1'b0) begin
on_proc <= 1'b0;
cnt <= 0;
cnt_x <= 0;
cnt_y <= 0;
finish <= 1'b0;
end else begin
if(start == 1'b1) on_proc <= 1'b1;
else if((cnt == 11) && (cnt_x == 255) && (cnt_y == 255)) on_proc <= 1'b0;
if(on_proc == 1'b1) begin
cnt <= (cnt == 11) ? 0 : cnt+1;
if(cnt == 11) begin
cnt_x <= (cnt_x == 255) ? 0 : cnt_x+1;
if(cnt_x == 255) begin
cnt_y <= (cnt_y == 255) ? 0 : cnt_y+1;
end
end
end
finish <= ((cnt == 11) && (cnt_x == 255) && (cnt_y == 255));
end
end
wire mem_rd = (cnt >= 0) && (cnt <= 8) && (on_proc == 1'b1);
reg [16:0] rd_addr;
always@(*) begin
case(cnt)
4'd0: rd_addr = (cnt_y-1)*256 + cnt_x-1;
4'd1: rd_addr = (cnt_y-1)*256 + cnt_x;
4'd2: rd_addr = (cnt_y-1)*256 + cnt_x+1;
4'd3: rd_addr = (cnt_y )*256 + cnt_x-1;
4'd4: rd_addr = (cnt_y )*256 + cnt_x;
4'd5: rd_addr = (cnt_y )*256 + cnt_x+1;
4'd6: rd_addr = (cnt_y+1)*256 + cnt_x-1;
4'd7: rd_addr = (cnt_y+1)*256 + cnt_x;
4'd8: rd_addr = (cnt_y+1)*256 + cnt_x+1;
default: rd_addr = 'bx;
endcase
end
reg [7:0] pd;
wire pd_en = (cnt >= 1) && (cnt <= 9);
always@(posedge clk or negedge n_reset) begin
if(n_reset == 1'b0) begin
pd <= 0;
end else begin
if(pd_en == 1'b1) pd <= dout;
end
end
reg signed [7:0] h[0:8];
always@(posedge clk or negedge n_reset) begin
if(n_reset == 1'b0) begin
h[0] <= 8'h08;
h[1] <= 8'h10;
h[2] <= 8'h08;
h[3] <= 8'h10;
h[4] <= 8'h20;
h[5] <= 8'h10;
h[6] <= 8'h08;
h[7] <= 8'h10;
h[8] <= 8'h08;
end else begin
if(h_write == 1'b1) begin
h[h_idx] <= h_data;
end
end
end
wire signed [7:0] coeff = h[cnt-2];
wire signed [15:0] mul = pd * coeff;
reg signed [19:0] acc;
wire signed [19:0] acc_in = (cnt == 1) ? 0 : mul + acc;
reg acc_en;
always@(*) begin
acc_en = 1'b0;
case(cnt)
4'd 1: acc_en = 1'b1;
4'd 2: if((cnt_y > 0) && (cnt_x > 0)) acc_en = 1'b1;
4'd 3: if((cnt_y > 0) ) acc_en = 1'b1;
4'd 4: if((cnt_y > 0) && (cnt_x < 255)) acc_en = 1'b1;
4'd 5: if(cnt_x > 0) acc_en = 1'b1;
4'd 6: acc_en = 1'b1;
4'd 7: if(cnt_x < 255) acc_en = 1'b1;
4'd 8: if((cnt_y < 255) && (cnt_x > 0)) acc_en = 1'b1;
4'd 9: if((cnt_y < 255) ) acc_en = 1'b1;
4'd10: if((cnt_y < 255) && (cnt_x < 255)) acc_en = 1'b1;
default: acc_en = 1'b0;
endcase
end
always@(posedge clk or negedge n_reset) begin
if(n_reset == 1'b0) begin
acc <= 'b0;
end else begin
if(acc_en == 1'b1) acc <= acc_in;
end
end
wire [19:0] pd_rnd_1 = acc + (1<<6);
wire [12:0] pd_rnd = pd_rnd_1[19:7];
wire [7:0] pd_out = (pd_rnd < 0) ? 0 :
(pd_rnd > 255) ? 255 :
pd_rnd[7:0];
assign din = pd_out;
wire mem_wr = (cnt == 11);
wire [16:0] wr_addr = cnt_y * 256 + cnt_x + 256*256;
assign cs = mem_rd | mem_wr;
assign we = mem_wr;
assign addr = (mem_rd == 1'b1) ? rd_addr : wr_addr;
endmodule
module top_filter_2d;
reg clk, n_reset;
reg start;
wire finish;
initial clk = 1'b0;
always #5 clk = ~clk;
initial begin
n_reset = 1'b1;
$readmemh("../c/img_in.dat", i_buf.data);
#3;
n_reset = 1'b0;
#20;
n_reset = 1'b1;
@(posedge clk);
@(posedge clk);
@(posedge clk);
start = 1'b1;
@(posedge clk);
start = 1'b0;
end
wire cs, we;
wire [16:0] addr;
wire [7:0] din;
wire [7:0] dout;
filter2d i_filter (.clk(clk), .n_reset(n_reset), .start(start), .finish(finish),
.cs(cs), .we(we), .addr(addr), .din(din), .dout(dout),
.h_write(1'b0), .h_idx(4'b0), .h_data(8'b0));
mem_single #(
.WD(8),
.DEPTH(256*256*2)
) i_buf (
.clk(clk),
.cs(cs),
.we(we),
.addr(addr),
.din(din),
.dout(dout)
);
always@(posedge clk) begin
if(finish == 1'b1) begin
for(int i=0;i<256;i++) begin
for(int j=0;j<256;j++) begin
$write("%3d ", i_buf.data[i*256+j+256*256]);
end
$write("\n");
end
$finish;
end
end
endmodule
module mem_single #(
WD = 128
, DEPTH = 64
, WA = $clog2(DEPTH)
) (
input clk
, input cs
, input we
, input [WA-1:0] addr
, input [WD-1:0] din
, output [WD-1:0] dout
);
reg [WD-1:0] data[DEPTH-1:0];
reg [WA-1:0] addr_d;
always@(posedge clk) begin
if(cs == 1'b1) begin
if(we == 1'b1) data[addr] <= din;
addr_d <= addr;
end
end
assign dout = data[addr_d];
endmodule
위 mem_single 모듈은 아래에서도 계속 사용합니다.
- 3.3 Double Buffering
module filter2d (
input clk,
input n_reset,
input i_strb,
input [7:0] i_data,
output o_strb,
output [7:0] o_data
);
wire start;
wire mem_rd;
wire [15:0] rd_addr;
wire [7:0] rd_data;
filter2d_buf i_buf(
.clk(clk),
.n_reset(n_reset),
.i_strb(i_strb),
.i_data(i_data),
.start(start),
.mem_rd(mem_rd),
.rd_addr(rd_addr),
.rd_data(rd_data)
);
filter2d_op i_op(
.clk(clk),
.n_reset(n_reset),
.start(start),
.mem_rd(mem_rd),
.rd_addr(rd_addr),
.rd_data(rd_data),
.o_strb(o_strb),
.o_data(o_data)
);
endmodule
module filter2d_op (
input clk,
input n_reset,
input start,
output mem_rd,
output reg [15:0] rd_addr,
input [7:0] rd_data,
output reg o_strb,
output reg [7:0] o_data,
input h_write,
input [3:0] h_idx,
input [7:0] h_data
);
reg on_proc;
reg [3:0] cnt;
reg [7:0] cnt_x;
reg [7:0] cnt_y;
always@(posedge clk or negedge n_reset) begin
if(n_reset == 1'b0) begin
on_proc <= 1'b0;
cnt <= 0;
cnt_x <= 0;
cnt_y <= 0;
end else begin
if(start == 1'b1) on_proc <= 1'b1;
else if((cnt == 11) && (cnt_x == 255) && (cnt_y == 255)) on_proc <= 1'b0;
if(on_proc == 1'b1) begin
cnt <= (cnt == 11) ? 0 : cnt+1;
if(cnt == 11) begin
cnt_x <= (cnt_x == 255) ? 0 : cnt_x+1;
if(cnt_x == 255) begin
cnt_y <= (cnt_y == 255) ? 0 : cnt_y+1;
end
end
end
end
end
assign mem_rd = (cnt >= 0) && (cnt <= 8) && (on_proc == 1'b1);
always@(*) begin
case(cnt)
4'd0: rd_addr = (cnt_y-1)*256 + cnt_x-1;
4'd1: rd_addr = (cnt_y-1)*256 + cnt_x;
4'd2: rd_addr = (cnt_y-1)*256 + cnt_x+1;
4'd3: rd_addr = (cnt_y )*256 + cnt_x-1;
4'd4: rd_addr = (cnt_y )*256 + cnt_x;
4'd5: rd_addr = (cnt_y )*256 + cnt_x+1;
4'd6: rd_addr = (cnt_y+1)*256 + cnt_x-1;
4'd7: rd_addr = (cnt_y+1)*256 + cnt_x;
4'd8: rd_addr = (cnt_y+1)*256 + cnt_x+1;
default: rd_addr = 'bx;
endcase
end
reg [7:0] pd;
wire pd_en = (cnt >= 1) && (cnt <= 9);
always@(posedge clk or negedge n_reset) begin
if(n_reset == 1'b0) begin
pd <= 0;
end else begin
if(pd_en == 1'b1) pd <= rd_data;
end
end
reg signed [7:0] h[0:8];
always@(posedge clk or negedge n_reset) begin
if(n_reset == 1'b0) begin
h[0] <= 8'h08;
h[1] <= 8'h10;
h[2] <= 8'h08;
h[3] <= 8'h10;
h[4] <= 8'h20;
h[5] <= 8'h10;
h[6] <= 8'h08;
h[7] <= 8'h10;
h[8] <= 8'h08;
end else begin
if(h_write == 1'b1) begin
h[h_idx] <= h_data;
end
end
end
wire signed [7:0] coeff = h[cnt-2];
wire signed [15:0] mul = pd * coeff;
reg signed [19:0] acc;
wire signed [19:0] acc_in = (cnt == 1) ? 0 : mul + acc;
reg acc_en;
always@(*) begin
acc_en = 1'b0;
case(cnt)
4'd 1: acc_en = 1'b1;
4'd 2: if((cnt_y > 0) && (cnt_x > 0)) acc_en = 1'b1;
4'd 3: if((cnt_y > 0) ) acc_en = 1'b1;
4'd 4: if((cnt_y > 0) && (cnt_x < 255)) acc_en = 1'b1;
4'd 5: if(cnt_x > 0) acc_en = 1'b1;
4'd 6: acc_en = 1'b1;
4'd 7: if(cnt_x < 255) acc_en = 1'b1;
4'd 8: if((cnt_y < 255) && (cnt_x > 0)) acc_en = 1'b1;
4'd 9: if((cnt_y < 255) ) acc_en = 1'b1;
4'd10: if((cnt_y < 255) && (cnt_x < 255)) acc_en = 1'b1;
default: acc_en = 1'b0;
endcase
end
always@(posedge clk or negedge n_reset) begin
if(n_reset == 1'b0) begin
acc <= 'b0;
end else begin
if(acc_en == 1'b1) acc <= acc_in;
end
end
wire [19:0] pd_rnd_1 = acc + (1<<6);
wire [12:0] pd_rnd = pd_rnd_1[19:7];
wire [7:0] pd_out = (pd_rnd < 0) ? 0 :
(pd_rnd > 255) ? 255 :
pd_rnd[7:0];
always@(posedge clk or negedge n_reset) begin
if(n_reset == 1'b0) begin
o_strb <= 1'b0;
o_data <= 'b0;
end else begin
o_strb <= (cnt == 11);
if(cnt == 11) begin
o_data <= pd_out;
end
end
end
endmodule
module filter2d_buf (
input clk,
input n_reset,
input i_strb,
input [7:0] i_data,
output reg start,
input mem_rd,
input [15:0] rd_addr,
output [7:0] rd_data
);
reg [7:0] cnt_x;
reg [7:0] cnt_y;
always@(posedge clk or negedge n_reset) begin
if(n_reset == 1'b0) begin
cnt_x <= 255;
cnt_y <= 255;
end else begin
if(i_strb == 1'b1) begin
cnt_x <= (cnt_x == 255) ? 0 : cnt_x+1;
if(cnt_x == 255) begin
cnt_y <= (cnt_y == 255) ? 0 : cnt_y+1;
end
end
end
end
reg mode;
wire mode_change;
reg mem_wr;
reg [7:0] wr_data;
assign mode_change = (mem_wr == 1'b1) && (cnt_x == 255) && (cnt_y == 255);
always@(posedge clk or negedge n_reset) begin
if(n_reset == 1'b0) begin
mode <= 1'b0;
start <= 1'b0;
end else begin
if(mode_change == 1'b1) begin
mode <= ~mode;
end
start <= mode_change;
end
end
always@(posedge clk or negedge n_reset) begin
if(n_reset == 1'b0) begin
mem_wr <= 1'b0;
wr_data <= 8'b0;
end else begin
mem_wr <= i_strb;
wr_data <= i_data;
end
end
wire [15:0] wr_addr = cnt_y*256 + cnt_x;
wire cs0 = (mode == 1'b0) ? mem_wr : mem_rd;
wire we0 = (mode == 1'b0) ? mem_wr : 1'b0;
wire [15:0] addr0 = (mode == 1'b0) ? wr_addr : rd_addr;
wire [7:0] din0 = (mode == 1'b0) ? wr_data : 'b0;
wire [7:0] dout0;
wire cs1 = (mode == 1'b1) ? mem_wr : mem_rd;
wire we1 = (mode == 1'b1) ? mem_wr : 1'b0;
wire [15:0] addr1 = (mode == 1'b1) ? wr_addr : rd_addr;
wire [7:0] din1 = (mode == 1'b1) ? wr_data : 'b0;
wire [7:0] dout1;
assign rd_data = (mode == 1'b0) ? dout1 : dout0;
mem_single #(
.WD(8),
.DEPTH(256*256)
) i_buf0 (
.clk(clk),
.cs(cs0),
.we(we0),
.addr(addr0),
.din(din0),
.dout(dout0)
);
mem_single #(
.WD(8),
.DEPTH(256*256)
) i_buf1 (
.clk(clk),
.cs(cs1),
.we(we1),
.addr(addr1),
.din(din1),
.dout(dout1)
);
endmodule
module top_filter_2d;
reg clk, n_reset;
reg start;
initial clk = 1'b0;
always #5 clk = ~clk;
reg [7:0] img_data[0:65535];
reg i_strb;
reg [7:0] i_data;
integer idx, cnt;
initial begin
cnt = 0;
n_reset = 1'b1;
$readmemh("../c/img_in.dat", img_data);
i_strb = 1'b0;
i_data = 'bx;
#3;
n_reset = 1'b0;
#20;
n_reset = 1'b1;
@(posedge clk);
@(posedge clk);
@(posedge clk);
repeat(3) begin
for(idx=0;idx<65536;idx=idx+1) begin
i_strb = 1'b1;
i_data = img_data[idx];
@(posedge clk);
repeat(16) begin
i_strb = 1'b0;
i_data = 'bx;
@(posedge clk);
end
end
end
@(posedge clk);
@(posedge clk);
@(posedge clk);
$finish;
end
wire o_strb;
wire [7:0] o_data;
filter2d i_filter (
.clk(clk),
.n_reset(n_reset),
.i_strb(i_strb),
.i_data(i_data),
.o_strb(o_strb),
.o_data(o_data),
.h_write(1'b0),
.h_idx(4'b0),
.h_data(8'b0)
);
always@(posedge clk) begin
if(o_strb == 1'b1) begin
$write("%3d ", o_data);
cnt = cnt + 1;
if(cnt[7:0] == 0) begin
$write("\n");
end
end
end
endmodule
- 3.4 Line Buffer
module filter2d (
input clk,
input n_reset,
input i_strb,
input [7:0] i_data,
output reg o_strb,
output reg [7:0] o_data,
input h_write,
input [3:0] h_idx,
input [7:0] h_data
);
reg garbage;
reg [3:0] cnt;
reg [7:0] cnt_x;
reg [7:0] cnt_y;
reg [7:0] i_data_d;
always@(posedge clk or negedge n_reset) begin
if(n_reset == 1'b0) begin
garbage <= 1'b1;
cnt <= 7;
cnt_x <= 254;
cnt_y <= 254;
i_data_d <= 'b0;
end else begin
if(i_strb == 1'b1) begin
cnt_x <= (cnt_x == 255) ? 0 : cnt_x+1;
if(cnt_x == 255) begin
cnt_y <= (cnt_y == 255) ? 0 : cnt_y+1;
if(cnt_y == 255) garbage <= 1'b0;
end
end
if(i_strb == 1'b1) cnt <= 0;
else if(cnt < 7) cnt <= cnt+1;
if(i_strb == 1'b1) i_data_d <= i_data;
end
end
reg [7:0] ibuf[2:0][2:0];
wire [7:0] dout;
always@(posedge clk or negedge n_reset) begin
if(n_reset == 1'b0) begin
for(int i=0;i<3;i++) begin
for(int j=0;j<3;j++) begin
ibuf[i][j] <= 'b0;
end
end
end else begin
if(cnt == 0) begin
for(int i=0;i<3;i++) begin
for(int j=0;j<2;j++) begin
ibuf[i][j] <= ibuf[i][j+1];
end
end
ibuf[2][2] <= i_data_d;
end
if(cnt == 1) ibuf[0][2] <= dout;
if(cnt == 2) ibuf[1][2] <= dout;
end
end
wire mem_rd = (cnt == 0) || (cnt == 1);
wire mem_wr = (cnt == 2);
reg [8:0] wr_addr;
wire [8:0] rd_addr0 = wr_addr;
wire [8:0] rd_addr1 = (wr_addr<256) ? wr_addr+256 : wr_addr-256;
wire [8:0] rd_addr = (cnt == 0) ? rd_addr0 : rd_addr1;
always@(posedge clk or negedge n_reset) begin
if(n_reset == 1'b0) begin
wr_addr <= 0;
end else begin
if(mem_wr == 1'b1) begin
wr_addr <= (wr_addr == 2*256-1) ? 0 : wr_addr + 1;
end
end
end
wire cs = mem_rd | mem_wr;
wire we = mem_wr;
wire [8:0] addr = (mem_wr == 1'b1) ? wr_addr : rd_addr;
wire [7:0] din = i_data_d;
mem_single #(
.WD(8),
.DEPTH(2*256)
) i_buf0 (
.clk(clk),
.cs(cs),
.we(we),
.addr(addr),
.din(din),
.dout(dout)
);
reg signed [7:0] h[0:8];
always@(posedge clk or negedge n_reset) begin
if(n_reset == 1'b0) begin
h[0] <= 8'h08;
h[1] <= 8'h10;
h[2] <= 8'h08;
h[3] <= 8'h10;
h[4] <= 8'h20;
h[5] <= 8'h10;
h[6] <= 8'h08;
h[7] <= 8'h10;
h[8] <= 8'h08;
end else begin
if(h_write == 1'b1) begin
h[h_idx] <= h_data;
end
end
end
reg signed [15:0] mul[2:0][2:0];
always@(posedge clk or negedge n_reset) begin
if(n_reset == 1'b0) begin
for(int i=0;i<3;i++) begin
for(int j=0;j<3;j++) begin
mul[i][j] <= 'b0;
end
end
end else begin
if((cnt == 3) && (garbage == 1'b0)) begin
mul[0][0] <= ((cnt_y > 0) && (cnt_x > 0)) ? ibuf[0][0] * h[0] : 'b0;
mul[0][1] <= ((cnt_y > 0) ) ? ibuf[0][1] * h[1] : 'b0;
mul[0][2] <= ((cnt_y > 0) && (cnt_x < 255)) ? ibuf[0][2] * h[2] : 'b0;
mul[1][0] <= (cnt_x > 0) ? ibuf[1][0] * h[3] : 'b0;
mul[1][1] <= ibuf[1][1] * h[4];
mul[1][2] <= (cnt_x < 255) ? ibuf[1][2] * h[5] : 'b0;
mul[2][0] <= ((cnt_y < 255) && (cnt_x > 0)) ? ibuf[2][0] * h[6] : 'b0;
mul[2][1] <= ((cnt_y < 255) ) ? ibuf[2][1] * h[7] : 'b0;
mul[2][2] <= ((cnt_y < 255) && (cnt_x < 255)) ? ibuf[2][2] * h[8] : 'b0;
end
end
end
reg signed [19:0] sum_in;
reg signed [19:0] sum;
always@(*) begin
sum_in = 0;
for(int i=0;i<3;i++) begin
for(int j=0;j<3;j++) begin
sum_in = sum_in + mul[i][j];
end
end
end
always@(posedge clk or negedge n_reset) begin
if(n_reset == 1'b0) begin
sum <= 'b0;
end else begin
if((cnt == 4) && (garbage == 1'b0)) begin
sum <= sum_in;
end
end
end
wire [19:0] pd_rnd_1 = sum + (1<<6);
wire [12:0] pd_rnd = pd_rnd_1[19:7];
wire [7:0] pd_out = (pd_rnd < 0) ? 0 :
(pd_rnd > 255) ? 255 :
pd_rnd[7:0];
always@(posedge clk or negedge n_reset) begin
if(n_reset == 1'b0) begin
o_strb <= 1'b0;
o_data <= 'b0;
end else begin
o_strb <= ((cnt == 5) && (garbage == 1'b0));
if((cnt == 5) && (garbage == 1'b0)) begin
o_data <= pd_out;
end
end
end
endmodule
- 3.5 Parameter, DPI
module filter2d #(
H = 256,
W = 256
) (
input clk,
input n_reset,
input i_strb,
input [7:0] i_data,
output reg o_strb,
output reg [7:0] o_data,
input h_write,
input [3:0] h_idx,
input [7:0] h_data
);
reg garbage;
reg [3:0] cnt;
reg [$clog2(W)-1:0] cnt_x;
reg [$clog2(H)-1:0] cnt_y;
reg [7:0] i_data_d;
always@(posedge clk or negedge n_reset) begin
if(n_reset == 1'b0) begin
garbage <= 1'b1;
cnt <= 7;
cnt_x <= W-2;
cnt_y <= H-2;
i_data_d <= 'b0;
end else begin
if(i_strb == 1'b1) begin
cnt_x <= (cnt_x == W-1) ? 0 : cnt_x+1;
if(cnt_x == W-1) begin
cnt_y <= (cnt_y == H-1) ? 0 : cnt_y+1;
if(cnt_y == H-1) garbage <= 1'b0;
end
end
if(i_strb == 1'b1) cnt <= 0;
else if(cnt < 7) cnt <= cnt+1;
if(i_strb == 1'b1) i_data_d <= i_data;
end
end
reg [7:0] ibuf[2:0][2:0];
wire [7:0] dout;
always@(posedge clk or negedge n_reset) begin
if(n_reset == 1'b0) begin
for(int i=0;i<3;i++) begin
for(int j=0;j<3;j++) begin
ibuf[i][j] <= 'b0;
end
end
end else begin
if(cnt == 0) begin
for(int i=0;i<3;i++) begin
for(int j=0;j<2;j++) begin
ibuf[i][j] <= ibuf[i][j+1];
end
end
ibuf[2][2] <= i_data_d;
end
if(cnt == 1) ibuf[0][2] <= dout;
if(cnt == 2) ibuf[1][2] <= dout;
end
end
wire mem_rd = (cnt == 0) || (cnt == 1);
wire mem_wr = (cnt == 2);
localparam BUF_LEN = 2*W;
reg [$clog2(BUF_LEN)-1:0] wr_addr;
wire [$clog2(BUF_LEN)-1:0] rd_addr0 = wr_addr;
wire [$clog2(BUF_LEN)-1:0] rd_addr1 = (wr_addr<W) ? wr_addr+W: wr_addr-W;
wire [$clog2(BUF_LEN)-1:0] rd_addr = (cnt == 0) ? rd_addr0 : rd_addr1;
always@(posedge clk or negedge n_reset) begin
if(n_reset == 1'b0) begin
wr_addr <= 0;
end else begin
if(mem_wr == 1'b1) begin
wr_addr <= (wr_addr == BUF_LEN-1) ? 0 : wr_addr + 1;
end
end
end
wire cs = mem_rd | mem_wr;
wire we = mem_wr;
wire [8:0] addr = (mem_wr == 1'b1) ? wr_addr : rd_addr;
wire [7:0] din = i_data_d;
mem_single #(
.WD(8),
.DEPTH(BUF_LEN)
) i_buf0 (
.clk(clk),
.cs(cs),
.we(we),
.addr(addr),
.din(din),
.dout(dout)
);
reg signed [7:0] h[0:8];
always@(posedge clk or negedge n_reset) begin
if(n_reset == 1'b0) begin
h[0] <= 8'h08;
h[1] <= 8'h10;
h[2] <= 8'h08;
h[3] <= 8'h10;
h[4] <= 8'h20;
h[5] <= 8'h10;
h[6] <= 8'h08;
h[7] <= 8'h10;
h[8] <= 8'h08;
end else begin
if(h_write == 1'b1) begin
h[h_idx] <= h_data;
end
end
end
reg signed [15:0] mul[2:0][2:0];
always@(posedge clk or negedge n_reset) begin
if(n_reset == 1'b0) begin
for(int i=0;i<3;i++) begin
for(int j=0;j<3;j++) begin
mul[i][j] <= 'b0;
end
end
end else begin
if((cnt == 3) && (garbage == 1'b0)) begin
mul[0][0] <= ((cnt_y > 0) && (cnt_x > 0)) ? ibuf[0][0] * h[0] : 'b0;
mul[0][1] <= ((cnt_y > 0) ) ? ibuf[0][1] * h[1] : 'b0;
mul[0][2] <= ((cnt_y > 0) && (cnt_x < W-1)) ? ibuf[0][2] * h[2] : 'b0;
mul[1][0] <= (cnt_x > 0) ? ibuf[1][0] * h[3] : 'b0;
mul[1][1] <= ibuf[1][1] * h[4];
mul[1][2] <= (cnt_x < W-1) ? ibuf[1][2] * h[5] : 'b0;
mul[2][0] <= ((cnt_y < H-1) && (cnt_x > 0)) ? ibuf[2][0] * h[6] : 'b0;
mul[2][1] <= ((cnt_y < H-1) ) ? ibuf[2][1] * h[7] : 'b0;
mul[2][2] <= ((cnt_y < H-1) && (cnt_x < W-1)) ? ibuf[2][2] * h[8] : 'b0;
end
end
end
reg signed [19:0] sum_in;
reg signed [19:0] sum;
always@(*) begin
sum_in = 0;
for(int i=0;i<3;i++) begin
for(int j=0;j<3;j++) begin
sum_in = sum_in + mul[i][j];
end
end
end
always@(posedge clk or negedge n_reset) begin
if(n_reset == 1'b0) begin
sum <= 'b0;
end else begin
if((cnt == 4) && (garbage == 1'b0)) begin
sum <= sum_in;
end
end
end
wire [19:0] pd_rnd_1 = sum + (1<<6);
wire [12:0] pd_rnd = pd_rnd_1[19:7];
wire [7:0] pd_out = (pd_rnd < 0) ? 0 :
(pd_rnd > 255) ? 255 :
pd_rnd[7:0];
always@(posedge clk or negedge n_reset) begin
if(n_reset == 1'b0) begin
o_strb <= 1'b0;
o_data <= 'b0;
end else begin
o_strb <= ((cnt == 5) && (garbage == 1'b0));
if((cnt == 5) && (garbage == 1'b0)) begin
o_data <= pd_out;
end
end
end
endmodule
module top_filter_2d;
reg clk, n_reset;
reg start;
initial clk = 1'b0;
always #5 clk = ~clk;
import "DPI" function void init_filter2d(input int h, input int w);
import "DPI" function byte get_input();
import "DPI" function byte get_output();
reg i_strb;
reg [7:0] i_data;
initial begin
n_reset = 1'b1;
init_filter2d(256, 256);
i_strb = 1'b0;
i_data = 'bx;
#3;
n_reset = 1'b0;
#20;
n_reset = 1'b1;
@(posedge clk);
@(posedge clk);
@(posedge clk);
repeat(3) begin
repeat(256*256) begin
i_strb = 1'b1;
i_data = get_input();
@(posedge clk);
repeat(16) begin
i_strb = 1'b0;
i_data = 'bx;
@(posedge clk);
end
end
end
@(posedge clk);
@(posedge clk);
@(posedge clk);
$finish;
end
wire o_strb;
wire [7:0] o_data;
filter2d i_filter (
.clk(clk),
.n_reset(n_reset),
.i_strb(i_strb),
.i_data(i_data),
.o_strb(o_strb),
.o_data(o_data),
.h_write(1'b0),
.h_idx(4'b0),
.h_data(8'b0)
);
reg [7:0] out_ref;
always@(posedge clk) begin
if(o_strb == 1'b1) begin
out_ref = get_output();
if(o_data != out_ref) begin
$display("Error!! o_data = %3d, out_ref = %3d", o_data, out_ref);
#10;
$finish;
end
end
end
endmodule
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
unsigned char *in_img;
unsigned char *out_img;
int height, width;
void filter2d(void) {
int h[3][3] = {0x08, 0x10, 0x08, 0x10, 0x20, 0x10, 0x08, 0x10, 0x08};
for(int i=0;i<height;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<width;j++) {
int sum = 0;
if(i>0 && j>0) sum += in_img[(i-1)*width+j-1]*h[0][0];
if(i>0) sum += in_img[(i-1)*width+j ]*h[0][1];
if(i>0 && j<width-1) sum += in_img[(i-1)*width+j+1]*h[0][2];
if(j>0) sum += in_img[(i )*width+j-1]*h[1][0];
sum += in_img[(i )*width+j ]*h[1][1];
if(j<width-1) sum += in_img[(i )*width+j+1]*h[1][2];
if(i<height-1 && j>0) sum += in_img[(i+1)*width+j-1]*h[2][0];
if(i<height-1) sum += in_img[(i+1)*width+j ]*h[2][1];
if(i<height-1 && j<width-1) sum += in_img[(i+1)*width+j+1]*h[2][2];
sum = (sum + (1<<6)) >> 7;
if(sum < 0) out_img[i*width+j] = 0;
else if(sum > 255) out_img[i*width+j] = 255;
else out_img[i*width+j] = sum;
}
}
}
void init_filter2d(int h, int w) {
int i, a;
FILE *inf;
inf = fopen("../c/img_in.txt", "r");
height = h;
width = w;
in_img = malloc(height*width*sizeof(unsigned char));
out_img = malloc(height*width*sizeof(unsigned char));
for(i=0;i<height*width;i++) {
fscanf(inf, "%d,", &a);
in_img[i] = a;
}
filter2d();
fclose(inf);
}
unsigned char get_input(void) {
static int i;
unsigned char res = in_img[i];
i++;
if(i==height*width) i = 0;
return res;
}
unsigned char get_output(void) {
static int i;
unsigned char res = out_img[i];
i++;
if(i==height*width) i = 0;
return res;
}
4. 결과
다양한 방법으로 Filter를 구현해 보았습니다.
우선은 convolution 연산을 verilog로 구현할 수 있게 되었고,
확장해서 C로 작성한 코드를 이용할 수도 있었습니다.
Filter 자체도 사용할 곳이 많겠지만
다음에는 본래 목적인 이미지 AI 모델을 구현해보겠습니다.
우선은 직접 구현의 방식으로 계획 중에 있고,
잘 안된다면 C코드를 불러오는 DPI 방식까지 고려해두겠습니다.
- 다음 글
(2) FPGA에서 CNN 구현 : https://chonh0531.tistory.com/21
Filter - (2) FPGA에서 CNN구현
진행년월: 24.08 목차1. 배경2. 과제 정의 및 개요3. 소스코드4. 시뮬레이션 결과 1. 배경CNN 모델 중 가장 기본적인 Lenet-5 모델을 구현해보려고 합니다.메모리 등을 고려해야 하기 때문에,성능 자
chonh0531.tistory.com
'RTL, Synthesis, P&R' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Filter - (2) FPGA에서 CNN구현 (0) | 2024.09.09 |
|---|---|
| Cortex-M0 SOC 활용 - (3) Snake game with API (0) | 2024.09.09 |
| Cortex-M0 SOC 활용 - (2) Peripheral with C,CMCIS (0) | 2024.09.09 |
| Cortex-M0 SOC 활용 - (1) AMBA3 AHB-Lite와 Pheripheral (0) | 2024.09.09 |
| 16KB Cache Memory Controller - (1) RTL 및 Coverage (0) | 2024.09.07 |